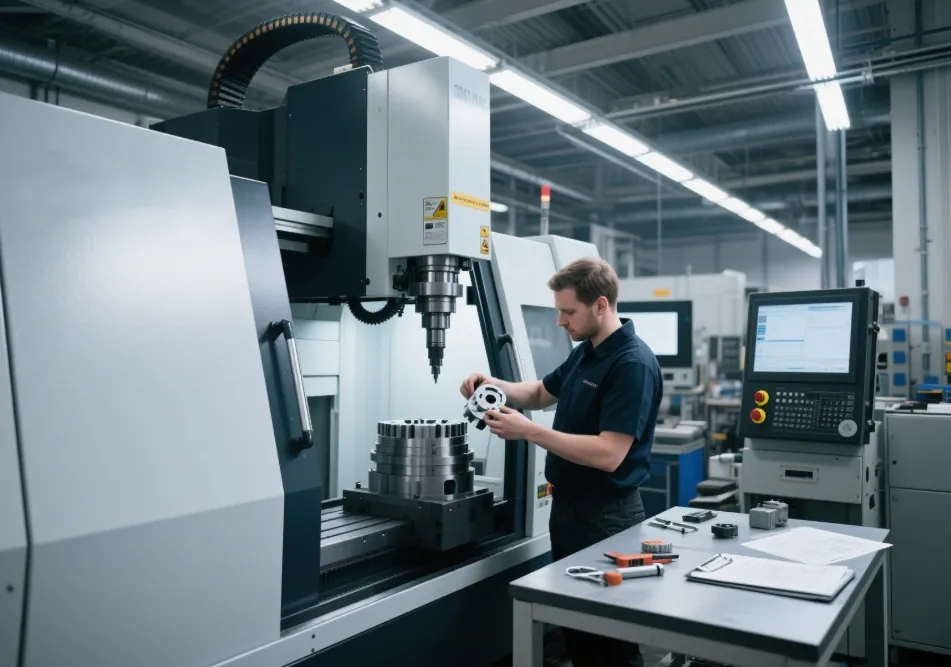
Complex parts. Tight tolerances. Unforgiving deadlines. In high-end manufacturing, CNC milling isn’t just a tool — it’s a strategic decision. But with so many variables in play, how do you choose the most effective milling approach?
From face milling to form milling, this article walks through the types of milling and the logic behind each choice so engineers can make smart, efficient decisions for any manufacturing challenge.

Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Milling by Cutting Method
Not all milling is created equal. The way a tool cuts into the material directly affects the quality, speed, and efficiency of machining. Let’s look at the most common types of milling, classified by their cutting methods.

Face Milling
Face milling is a machining process that uses a rotating cutter with cutting edges on both its face and periphery to produce flat, smooth surfaces. It’s particularly effective for creating broad, high-quality finishes on components where surface integrity matters, such as engine blocks or sealing surfaces.
One of the key advantages of face milling is its adaptability: by adjusting the tool’s inclination angle, operators can minimize vibrations and enhance chip evacuation, which is especially useful when machining tough or heat-resistant alloys.
Form Milling
Form milling uses specially shaped cutters designed to replicate complex profiles and contours in a single pass. Unlike face milling, which produces flat surfaces, form milling creates intricate shapes, such as gear teeth, grooves, keyways, and curved profiles, that are difficult or inefficient to machine with standard tools.
Angular Milling
Angular milling, also called angle milling, creates flat surfaces set at non-right angles to the tool or workpiece axis, enabling features like chamfers, bevels, dovetails, and V-grooves.
This process uses specialized cutters or adjustable machine setups to achieve precise angled cuts. It is widely applied in aerospace, automotive, medical, and mold making.
However, it demands careful setup, rigid machines, and sometimes costly cutters to maintain quality and control chip removal.
Peripheral Milling
Peripheral milling, also called plain or slab milling, removes material using cutters with teeth on their sides, with the cutter axis parallel to the workpiece surface.
It is ideal for shaping contours, slots, and flat surfaces through up or down-milling, which influences finish and tool life in different ways.
This versatile process requires rigid setups and effective chip removal to maintain precision and surface quality, making it essential in modern machining.
Slot Milling
Slot milling uses specialized slot cutters or end mills to create narrow channels or keyways with precise dimensions. Because these slots are often deep and precise, the setup needs to be very rigid to keep the dimensions accurate, especially when working with tough materials like titanium.
This technique is widely used to make keyways for shafts, where tight tolerances, often around ±0.05 mm, are crucial to ensure a perfect fit.
Types of Milling by Machine Setup
Beyond cutting techniques, the machine setup, specifically the number of axes, shapes the scope of milling operations.

3-Axis Milling
This setup moves the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z linear axes. It’s ideal for simple to moderately complex parts with flat or contoured surfaces but limited to machining features accessible from one side.
4-Axis Milling
4-axis milling enables rotation of the tool or workpiece around one axis (usually X or Y), allowing machining on multiple sides without repositioning. It is suited for parts with angled surfaces or complex contours.
5-Axis Milling
5-axis milling adds two rotational axes to three linear ones, allowing the tool to reach almost any angle. This boosts flexibility, reduces setups, and improves precision, ideal for complex parts in aerospace, medical, and mold industries.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Milling Method
Milling isn’t one-size-fits-all. The choice depends on both how the tool cuts and how the machine moves. Here’s a quick guide to help you match the best methods and setups to your project.
Geometry complexity
For simple flat surfaces or slots, conventional methods like face or slot milling suffice. More intricate shapes with curves and profiles call for specialized techniques like form or angular milling.
Tolerance requirements
Tight tolerances demand precise methods—face milling and 5-axis milling excel here by ensuring accuracy and surface finish.
Production volume
Smaller batches often use flexible 3-axis or specific cutting methods, while larger runs benefit from automated 4- or 5-axis setups combined with efficient cutting techniques.
Industry examples
- Aerospace: Complex parts require 5-axis milling and angular or form milling for precision and efficiency.
- Medical devices: Use form milling and 3- or 4-axis setups to balance detail and cost.
- Electronics: Simple profiles and slots are efficiently machined with slot or peripheral milling on 3-axis machines.
By integrating both cutting methods and machine setups, engineers can optimize milling strategies to meet diverse production demands.

Work with APT-Mold for Precision CNC Milling Services
Different types of milling bring distinct strengths tailored to part complexity, precision demands, and batch size. Picking the right technique unlocks smoother workflows and better results.
Collaborating with an experienced CNC service ensures you tap into the right know-how and technology. Whether it’s basic shapes or advanced multi-axis machining, having support streamlines production and boosts quality.
At APT-Mold, we provide expert CNC machining, including advanced CNC milling services with 3-, 4-, and 5-axis capabilities for complex parts and tight tolerances. Our expertise covers over 60 materials, along with finishing options like anodizing and plating.
Serving industries from automotive to healthcare, we focus on precision, cost-efficiency, and fast turnaround. With DFM support and rigorous quality checks, we’re your reliable partner for machining projects.
Reach out today for expert metal milling and custom CNC milling solutions tailored to your project needs.